Passive & Active Solar
We incorporate passive solar principals into all of our projects.
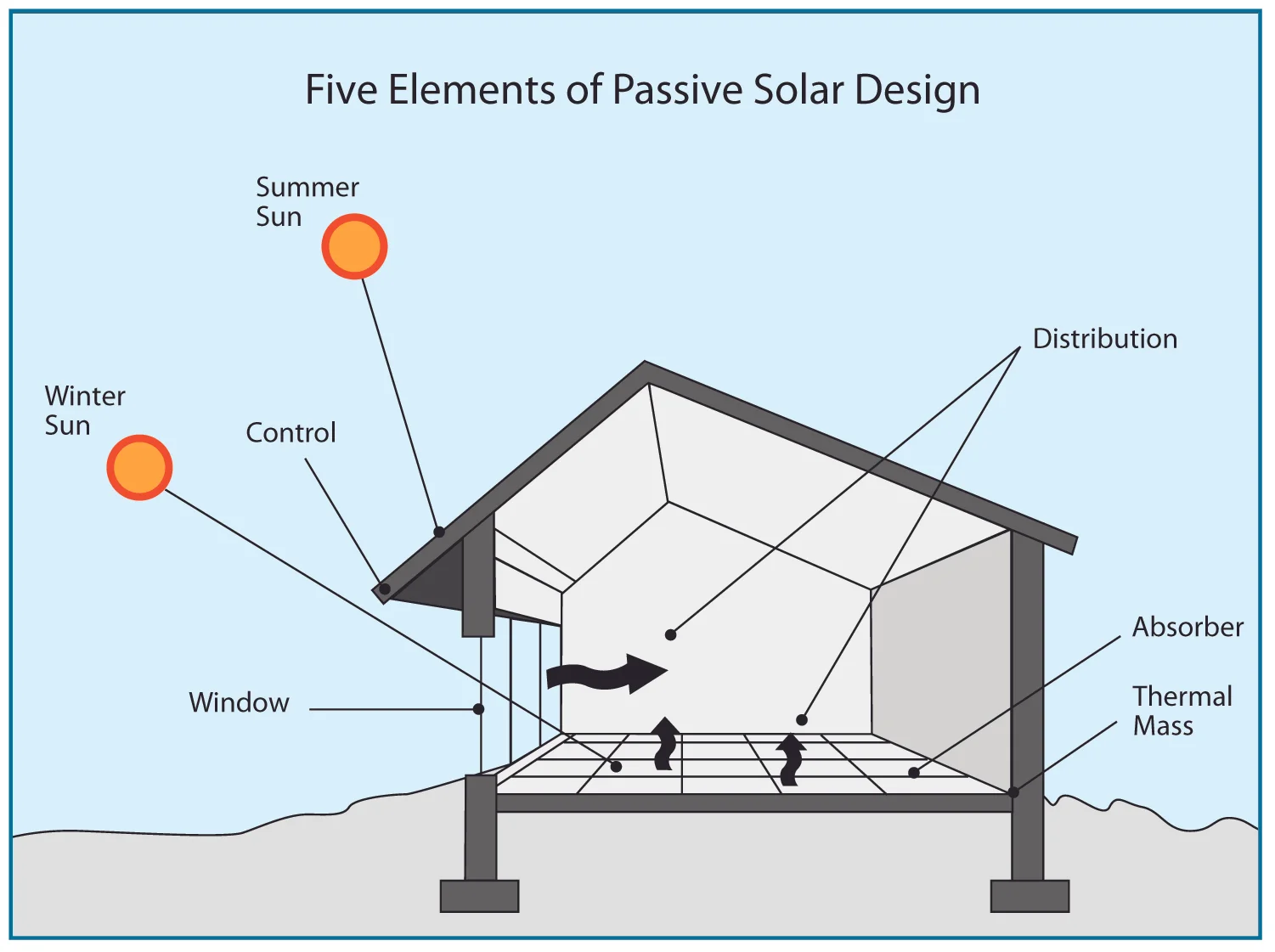
Every passive solar building includes five distinct design elements: An aperture or collector — the large glass area through which sunlight enters the building.
An absorber — the dark surface of the storage element that absorbs the solar heat.
A thermal mass — the material that stores the absorbed heat. This can be masonry materials such as concrete, stone, and brick; or a water tank.
A distribution method — the natural tendency of heat to move from warmer materials to cooler ones (through conduction, convection, and radiation) until there is no longer a temperature difference between the two. In some buildings, this strictly passive distribution method is augmented with fans, ducts, and blowers to circulate the heat.
A control mechanism — to regulate the amount of sunlight entering the aperture. This can be as simple as roof overhang designed to allow more sunlight to enter in the winter, less in the summer.
Solar Photovoltaic Panels (PV)
PV systems refer to photovoltaic module assembly utilized to generate and supply electricity in commercial and residential applications. With the increase in technologies and a greater Return on Investment (ROI) that fossel fuels in some sectors, the industry has rapidly expanded globally.
With proper planning the merging of systems can be greater than just the sum of their parts. With the addition of green roofing you can maintain a lower air temperature cooling the photovoltaic panels thus making them more efficient.
Solar technologies can be adapted for expanded use in everyday features not typically considered; such as being utilized for canopies for parking, markets, pedestrian, festival, transit waiting areas, etc.